What is an Embedded System? A Beginner’s Guide to Hardware, Software, and Key Knowledge
study
What is an Embedded System?
An embedded system is a computer system that integrates hardware and software, designed to perform specific functions within a larger system.
Definition
An embedded system is a specialized computer system tailored for a particular task. Unlike general-purpose computers (e.g., PCs), it is embedded into devices to carry out dedicated functions.
- "Embedded" means "built-in" or "integrated."
- Used in small appliances, automobiles, industrial machines, medical devices, etc.
embedded system
Components
1. Hardware
- Microcontroller (MCU) or Microprocessor (MPU)
- Sensors and actuators
- Memory (RAM, Flash, etc.)
2. Software
- Firmware (software for hardware control)
- Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)
- Application logic
3. Characteristics
- Real-time capability: Must perform actions within precise time limits (e.g., ABS brake systems)
- Dedicated functionality: Designed for a specific function (e.g., microwave control)
- Lightweight: Operates under constrained resources (memory, power, etc.)
- Embedded nature: Hidden inside the device and not visible to users
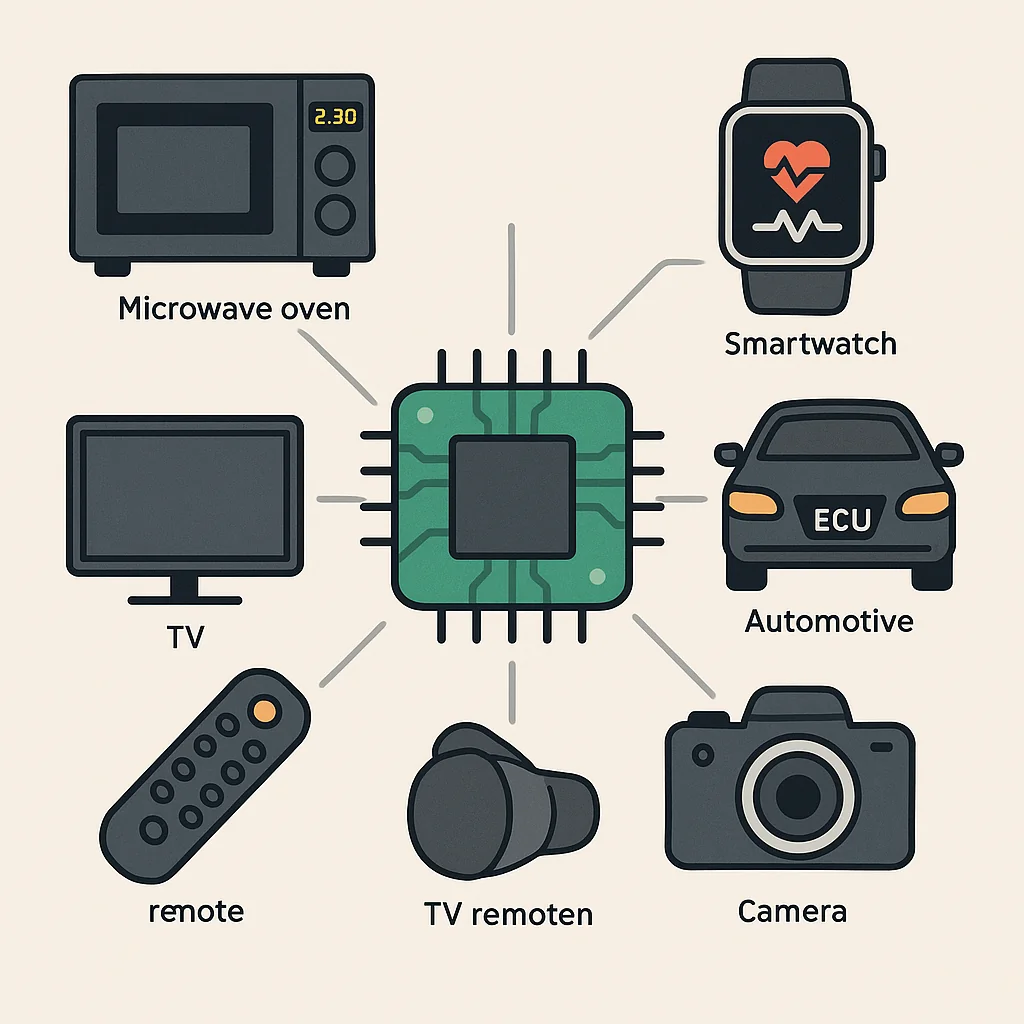
4. Examples
| Device | Embedded Function |
|---|---|
| Microwave Oven | Time and power control |
| Smartwatch | Heart rate monitoring, alerts |
| Car ECU | Engine and brake control |
| Digital Camera | Image processing and storage |
| TV Remote Control | IR signal, button detection |
📌 5. Comparison with General-Purpose Computers
| Category | Embedded System | General-Purpose Computer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Specific task | Multiple tasks |
| OS | None or RTOS | Windows, Linux, etc. |
| Expandability | Low | High |
| Use Cases | Refrigerator, car | Desktop, laptop |
✅ Knowledge Required to Learn Embedded Systems
1. 🧮 Mathematics
| Area | Topic | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Math | Arithmetic, exponentials, logarithms, ratios | ★★★ |
| Calculus | Derivatives, rates of change, sensor filtering | ★★★★ |
| Integration | Signal processing, accumulated values | ★★★ |
| Trigonometry | Sensor calculations (gyro, accelerometer), waves | ★★★★ |
| Matrices (basic) | Robotics control, transformations | ★★ |
| Probability/Stats | Noise handling, Kalman Filter | ★★ |
| Discrete Math | State machines, timer logic | ★★ |
| Laplace/Fourier | Signal filtering, frequency analysis (advanced) | ★ (opt.) |
2. ⚙️ Engineering / Computer Knowledge
| Area | Topic | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Logic Design | AND, OR, Flip-Flops, FSM | ★★★★ |
| Microcontrollers (MCU) | ATmega, STM32, ESP32 | ★★★★★ |
| C Programming | Core language for firmware | ★★★★★ ![ |
| Memory Structure | RAM, Flash, stack vs heap | ★★★ |
| Hardware Control | GPIO, PWM, ADC, UART | ★★★★★ |
| RTOS Concepts | FreeRTOS, task scheduling | ★★★ |
| Basic Electronics | Resistors, current, voltage, LED circuits | ★★★★ |
| Sensor Principles | Temperature, distance, gyro, accelerometer | ★★★★ |
| Communication Protocols | I2C, SPI, UART, CAN, BLE | ★★★★ |
| Debugging Techniques | Serial output, logic analyzer | ★★★ |
| Power Management | Voltage regulation, power consumption | ★★ |
| Embedded Linux (opt.) | Raspberry Pi, Yocto | ★ (opt.) |